Introduction
In today’s digitally connected world, networks are growing faster and becoming more complex than ever before. Cloud adoption, remote work, IoT devices, and virtualization have dramatically increased the number of endpoints that require reliable connectivity. At the core of this connectivity lies DDI – an integrated solution combining DNS (Domain Name System), DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol), and IPAM (IP Address Management). DDI is often described as the backbone of network operations. Without it, organizations would struggle with visibility, scalability, performance, and security. This article explores what DDI is, how its components work together, and why it is essential for modern IT environments.
What Is DDI?
DDI refers to the tight integration of three critical network services:
- DNS – Translates human-readable domain names into IP addresses
- DHCP – Automatically assigns IP addresses to devices on a network
- IPAM – Tracks, manages, and plans IP address usage
Individually, each service is important. Together, they form a unified system that enables seamless communication across enterprise, cloud, and hybrid networks.
Modern DDI platforms centralize management, automate workflows, and provide real-time visibility, making them indispensable for IT teams.
DNS: The Internet’s Address Book
The Domain Name System (DNS) is one of the most fundamental services in networking. It allows users to access websites and applications using easy-to-remember names instead of numeric IP addresses.
How DNS Works
When a user enters a domain name (e.g., www.example.com) into a browser:
- DNS queries are sent to find the corresponding IP address.
- The DNS server responds with the correct IP.
- The browser connects to the destination server.
This process happens in milliseconds and is critical for application performance.
Why DNS Matters
- Enables access to websites and applications
- Supports load balancing and traffic steering
- Plays a major role in cybersecurity (DNS filtering, threat detection)
DNS outages can bring entire businesses to a halt, making reliability and security paramount.
DHCP: Automating Network Connectivity
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) eliminates the need for manual IP address configuration.
What DHCP Does
When a device joins a network, DHCP automatically provides:
- An IP address
- Subnet mask
- Default gateway
- DNS server details
This automation ensures devices can communicate without human intervention.
Benefits of DHCP
- Reduces configuration errors
- Saves time for network administrators
- Supports mobile and dynamic environments
- Prevents IP address conflicts
In modern workplaces with thousands of endpoints – laptops, phones, printers, and IoT devices – DHCP is essential for scalability.
IPAM: Visibility and Control Over IP Addresses
IP Address Management (IPAM) is often the most overlooked component of DDI, yet it is critical for long-term network planning and stability.
What IPAM Provides
- Centralized tracking of IP address usage
- Management of IPv4 and IPv6 space
- Historical data and audit trails
- Integration with DNS and DHCP
Without IPAM, organizations rely on spreadsheets or manual tracking, which quickly becomes error-prone and unmanageable.
Why IPAM Is Important
- Prevents IP address exhaustion
- Improves network documentation
- Enables faster troubleshooting
- Supports compliance and audits
As networks grow and IPv6 adoption increases, IPAM becomes indispensable.
Why DDI Works Better Together
While DNS, DHCP, and IPAM can operate independently, managing them as separate systems creates silos, inconsistencies, and operational risks. Integrated DDI solves these challenges.
Key Advantages of Integrated DDI
- Centralized management from a single interface
- Automation of IP provisioning and DNS updates
- Improved accuracy with real-time synchronization
- Faster troubleshooting through unified visibility
For example, when a new device receives an IP address via DHCP, DDI automatically updates DNS records and IPAM databases – without manual input.
DDI and Network Security
DDI plays a growing role in cybersecurity.
Security Benefits of DDI
- DNS-based threat detection and blocking
- Prevention of rogue DHCP servers
- Visibility into suspicious network activity
- Enforcement of access policies
Because nearly all network traffic relies on DNS, it is an ideal control point for detecting malware, phishing, and command-and-control communications.
DDI in Cloud and Hybrid Environments
Modern IT infrastructures are no longer confined to on-premises data centers. DDI has evolved to support:
- Public cloud (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud)
- Private cloud
- Hybrid and multi-cloud environments
Cloud-aware DDI solutions provide consistent IP management and DNS resolution across environments, ensuring seamless connectivity and governance.
Who Needs DDI?
DDI is valuable for organizations of all sizes, including:
- Enterprises with large or distributed networks
- Cloud-first organizations
- Service providers and ISPs
- Healthcare, finance, and government sectors
- Organizations managing IoT and smart devices
As networks grow more dynamic, DDI becomes less of a luxury and more of a necessity.
The Future of DDI
The future of DDI is driven by automation, intelligence, and security.
Emerging trends include:
- AI-driven DNS analytics
- Zero Trust network integration
- Deeper cloud-native support
- Enhanced IPv6 management
As digital transformation accelerates, DDI will continue to serve as a critical foundation for reliable, secure, and scalable networking.
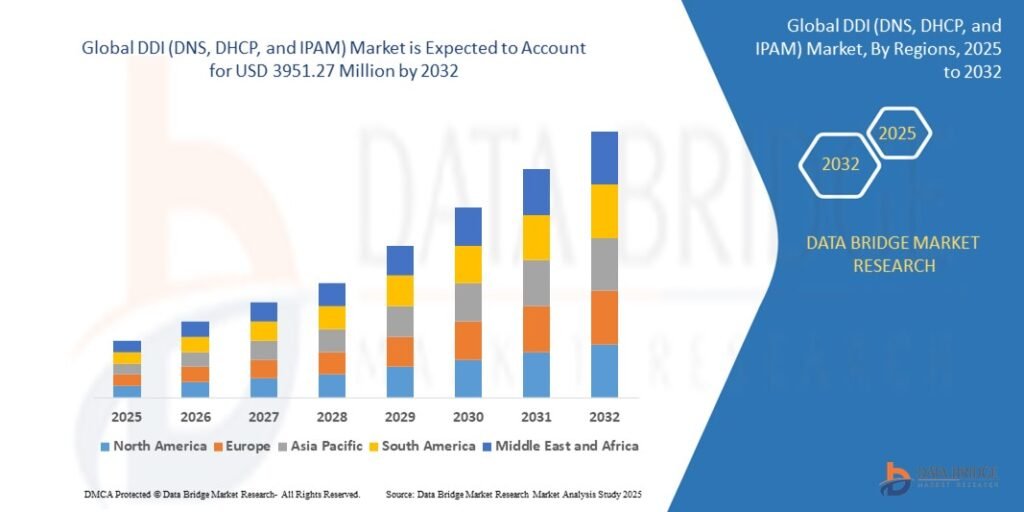
Growth Rate of DDI (DNS, DHCP and IPAM) Market
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the size of the global DDI (DNS, DHCP, and IPAM) market was estimated at USD 469.73 million in 2024 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 30.50% to reach USD 3951.27 million by 2032.
Learn More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-ddi-dns-dhcp-and-ipam-market
Conclusion
DDI (DNS, DHCP, and IPAM) is the unsung hero of modern networks. It ensures devices connect seamlessly, applications perform reliably, and administrators maintain control over complex environments. By integrating these three essential services, DDI delivers automation, visibility, security, and scalability.