Introduction
India is rapidly becoming one of the most attractive expansion destinations for international companies. With its growing economy, skilled workforce, and large consumer market, global brands are increasingly looking to establish their presence in the country. One of the most effective entry strategies is to open a branch office in India.
For UK and European companies planning to expand operations without forming a separate legal entity, a branch office offers flexibility, operational control, and cost efficiency. However, regulatory approvals, compliance requirements, and financial rules must be carefully understood before establishing a branch.
This guide explains everything foreign businesses need to know about setting up a branch office in India and how professional consulting support can simplify the process.
What is a Branch Office in India?
A branch office is an extension of a foreign company that allows it to conduct business operations in India while remaining legally part of the parent company. Unlike subsidiaries, branch offices do not create a separate corporate entity.
Foreign companies can operate through branch offices mainly to conduct permitted commercial activities while maintaining direct control over Indian operations.
Why UK and European Companies Choose Branch Offices in India
1. Direct Market Entry
Branch offices allow foreign companies to establish an immediate business presence in India without forming a new company structure.
2. Strong Brand Continuity
Since branch offices operate under the parent company’s identity, international brands can maintain global reputation and consistency.
3. Lower Setup Complexity
Compared to forming subsidiaries, branch offices usually require fewer corporate structuring formalities.
4. Access to India’s Expanding Market
India offers access to one of the world’s largest consumer markets and a rapidly growing business ecosystem.
Permitted Activities for Branch Offices
Foreign companies planning to open a branch office in India can perform specific business activities approved by regulators, including:
- Export and import of goods
- Professional and consultancy services
- Research and development collaborations
- Promoting technical or financial partnerships
- Acting as a buying or selling agent
- Providing IT and software services
Branch offices are restricted from conducting manufacturing activities directly but can outsource production to Indian vendors.
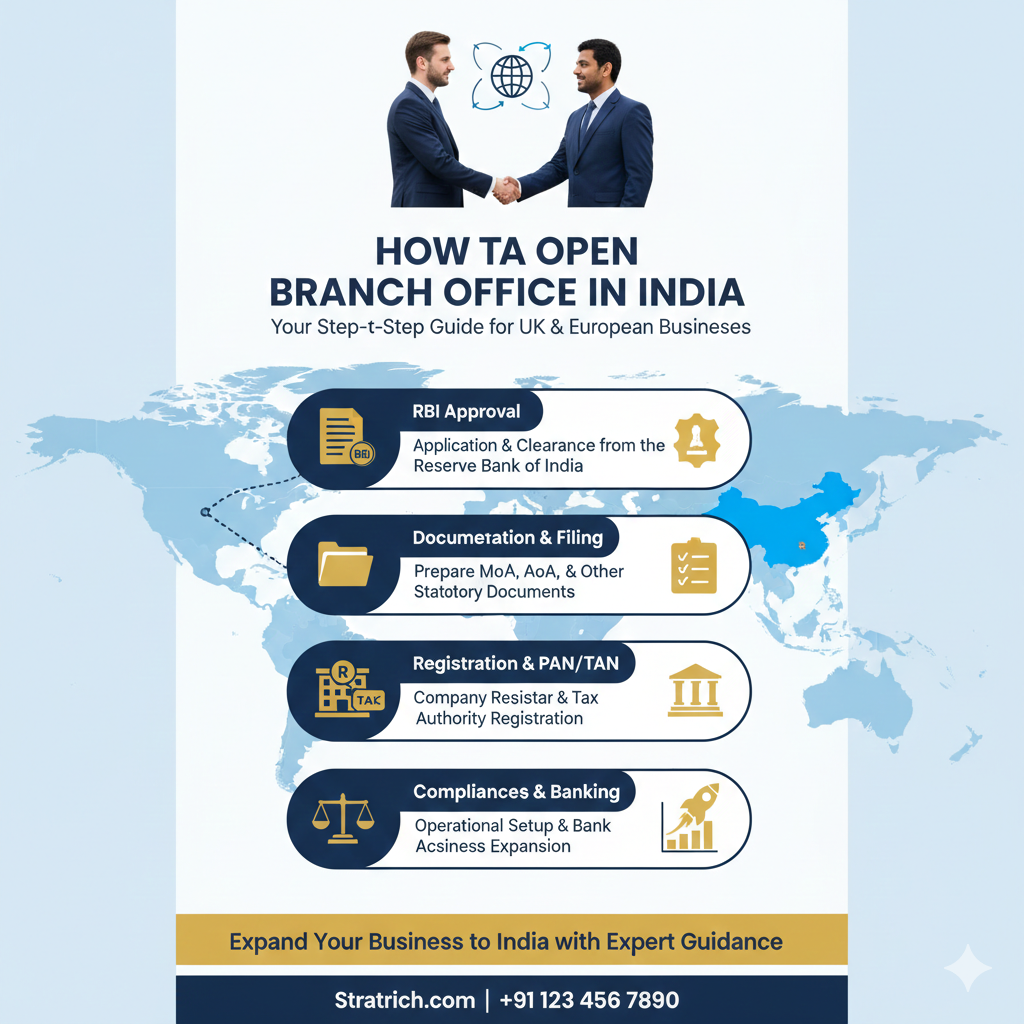
RBI Approval Requirements
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) regulates foreign branch office setups. Most foreign companies must obtain approval before starting operations.
Approval usually depends on:
- Parent company’s financial strength
- Proven business track record
- Industry sector compliance
- Minimum net worth requirements
Professional documentation and regulatory coordination are essential to ensure approval without delays.
Documents Required to Open a Branch Office in India
Foreign companies must prepare several legal and financial documents, including:
- Certificate of Incorporation of parent company
- Memorandum and Articles of Association
- Audited financial statements
- Board resolution approving branch setup
- Authorisation letter for Indian representative
- Detailed business activity plan
All documents typically require notarisation and apostille certification.
Step-by-Step Process to Open a Branch Office in India
Step 1: Evaluate Eligibility
The parent company must meet financial and operational criteria set by regulators.
Step 2: Prepare Regulatory Application
Submission of application to RBI through authorised banking channels.
Step 3: Obtain Government Approvals
Once RBI approval is received, companies must register with additional government departments.
Step 4: Register with Registrar of Companies
Branch offices must complete company registration and compliance documentation.
Step 5: Tax and Compliance Registration
Foreign companies must obtain tax identification, GST registration, and regulatory licenses if required.
Step 6: Open Indian Bank Account
A branch office must operate through authorised Indian banking channels for financial transactions.
Compliance Requirements After Registration
Branch offices must follow ongoing compliance rules such as:
- Filing annual financial statements
- Maintaining foreign exchange compliance reports
- Tax filing and auditing requirements
- RBI reporting obligations
- Regulatory renewal documentation
Non-compliance may result in penalties or operational restrictions.
Taxation Rules for Branch Offices
Branch offices are taxed as foreign entities operating in India. The taxation structure includes:
- Corporate tax on income generated in India
- Goods and Services Tax (GST) obligations
- Withholding tax on applicable payments
Professional tax planning is essential to optimise operational profitability.
Common Challenges Faced by Foreign Companies
Despite benefits, businesses often face challenges such as:
- Complex regulatory approvals
- Documentation authentication
- Compliance monitoring
- Understanding taxation rules
- Coordinating with multiple government authorities
Expert consulting guidance helps businesses avoid costly delays and legal complications.
How Stratrich Helps Foreign Businesses
Stratrich specialises in helping UK and European companies expand smoothly into India. Our services include:
- Branch office eligibility assessment
- RBI approval management
- Documentation preparation
- Company registration support
- Tax and compliance assistance
- End-to-end market entry consultation
Our strategic approach ensures businesses launch operations quickly while staying fully compliant with Indian regulations.
Conclusion
Choosing to open a branch office in India is a strategic decision for UK and European companies aiming to enter one of the world’s fastest-growing markets. While the process involves regulatory approvals and compliance management, the long-term business advantages make it a valuable expansion strategy.
With expert support and structured planning, foreign businesses can establish a strong operational presence and unlock growth opportunities in India’s evolving economic landscape.