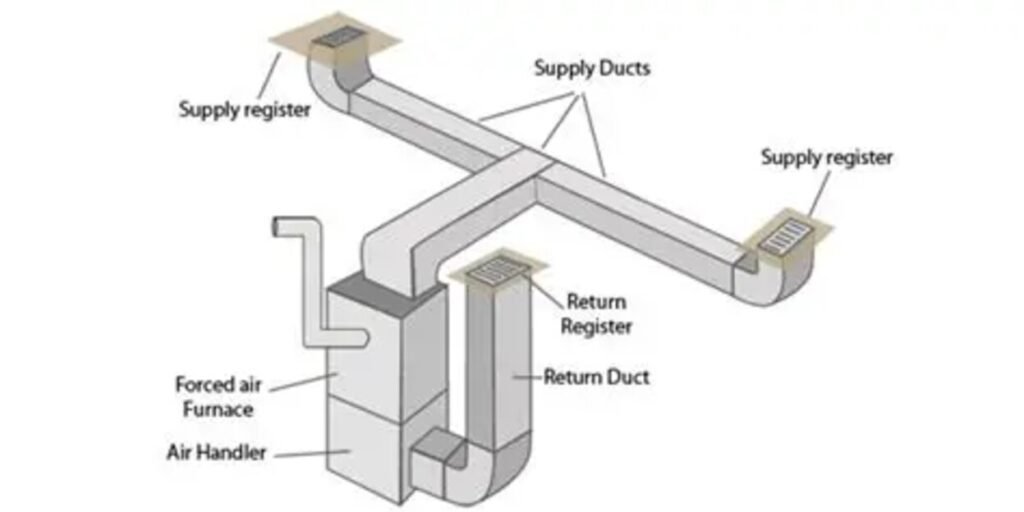
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems are the backbone of modern comfort, ensuring that homes, offices, and industrial facilities maintain optimal indoor air quality and temperature. At the heart of this system lies the Supply Duct—a critical component responsible for delivering conditioned air efficiently and consistently. Understanding its design and function is essential for HVAC professionals, building managers, and anyone invested in energy-efficient climate control.
Best choice: ac 1/2 pk – acjakarta
What Is a Supply Duct?
A Supply Duct is the network of passages that distributes cooled or heated air from the HVAC unit into occupied spaces. Unlike return ducts, which carry air back to the system for reconditioning, supply ducts push treated air forward, ensuring occupants experience the desired comfort levels.
Key functions include:
- Delivering conditioned air evenly across rooms
- Maintaining balanced airflow and pressure
- Supporting energy efficiency by minimizing leakage and resistance
Principles of Supply Duct Design
Designing an effective Supply Duct system requires a balance of engineering precision and practical installation. Poorly designed ducts can lead to uneven temperatures, wasted energy, and increased operational costs.
Airflow Calculations
Accurate airflow measurement is the foundation of duct design. Engineers calculate cubic feet per minute (CFM) requirements based on room size, occupancy, and load conditions.
Duct Sizing
Undersized ducts restrict airflow, while oversized ducts waste material and reduce efficiency. Proper sizing ensures optimal velocity, typically between 600–900 feet per minute for residential and light commercial systems.
Material Selection
Common materials include galvanized steel, aluminum, and flexible ducting. Each has advantages:
- Steel: Durable, ideal for large-scale installations
- Aluminum: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant
- Flexible ducts: Easy to install in tight spaces
Layout and Routing
Straight runs minimize resistance, while smooth bends reduce turbulence. Designers aim for minimal friction loss by avoiding sharp turns and excessive length.
Components of a Supply Duct System
A complete Supply Duct system integrates several elements to ensure performance:
- Main Trunk Line: The central channel carrying air from the HVAC unit.
- Branch Ducts: Smaller ducts that distribute air to individual rooms.
- Diffusers and Registers: End-point devices that control airflow direction and volume.
- Dampers: Adjustable plates that regulate airflow, balancing distribution across zones.
- Insulation: Prevents energy loss and condensation, improving efficiency.
Global Considerations in Supply Duct Design
HVAC requirements vary across climates and building types, making duct design a global challenge.
- Tropical Regions: Emphasis on cooling efficiency and moisture control.
- Cold Climates: Supply ducts must minimize heat loss and prevent freezing.
- Commercial Buildings: Require zoning strategies to handle diverse occupancy patterns.
- Industrial Facilities: Demand robust ductwork capable of handling high airflow volumes.
By tailoring duct design to local conditions, HVAC professionals ensure systems remain reliable and cost-effective worldwide.
Best Practices for Supply Duct Efficiency
Efficiency is not just about delivering air—it’s about doing so with minimal energy waste. Here are proven strategies:
- Seal All Joints: Air leakage is a common culprit in energy loss. Proper sealing with mastic or tape is essential.
- Use Proper Insulation: Insulated ducts reduce thermal loss and prevent condensation.
- Balance Airflow: Dampers and registers should be adjusted to maintain consistent comfort across zones.
- Regular Maintenance: Dust, debris, and wear can compromise airflow. Scheduled inspections keep ducts performing optimally.
Supply Ducts and Product Innovation
Modern HVAC products are evolving to meet stricter energy standards and sustainability goals. Manufacturers now offer:
Pre-insulated duct panels for faster installation and reduced thermal loss
Flexible duct systems with antimicrobial linings for improved indoor air quality
Smart dampers integrated with building automation systems for precise airflow control
These innovations highlight how supply ducts are no longer passive components but active contributors to building performance.
Why Supply Duct Design Matters
A well-designed Supply Duct system delivers more than comfort—it impacts energy bills, equipment lifespan, and occupant health. Poor airflow can strain HVAC units, increase maintenance costs, and create uneven temperatures. Conversely, optimized ductwork ensures:
- Consistent indoor climate
- Reduced energy consumption
- Enhanced air quality
- Long-term system reliability
Conclusion
The Supply Duct is the unsung hero of HVAC systems, quietly ensuring that conditioned air reaches every corner of a building. From sizing and materials to layout and maintenance, each design choice influences performance and efficiency. As global demand for sustainable and cost-effective climate control grows, supply duct innovation will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of HVAC.
For professionals, mastering supply duct design is not just technical expertise—it’s a commitment to delivering comfort, efficiency, and reliability across diverse environments.